Modeling Real Estate Transactions in Beancount
Real estate transactions may constitute the largest financial activity in a family's lifetime. This article explains how to model real estate in Beancount. I treat real estate as an asset and the appreciation of the house as unrealized gain. Additionally, the mortgage is modeled as a liability, and the interest is considered an expense.
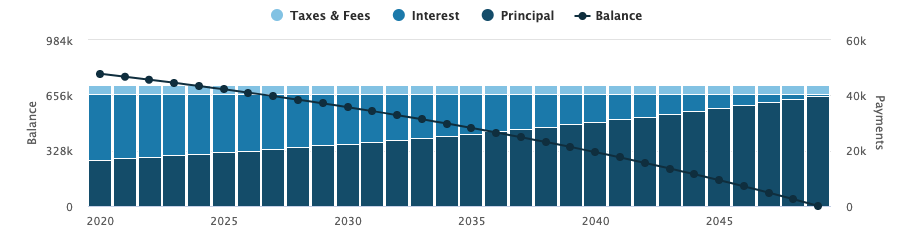
Let's assume that Mr. A purchased a luxury home located at 123 ABC Street, XYZ City, CA, 12345 on January 1, 2020, for a price of 1 million. The interest rate is 3.0%, the down payment is 20%, and the loan amount is 800,000.
| Item | Amount |
|---|---|
| Mortgage Amount | 800,000 |
| Interest Rate | 3% |
| Mortgage Period | 30 years |
| Total Cost of Mortgage | 1,478,219.62 |
| Monthly Payments | 4,106.17 |
| Home Insurance | 1,300 per year (39,000 total) |
| Property Tax | 7,500 per year (225,000 total) |
| Loan Payoff | 2049 Dec |
| Total Interest Paid | 414,219.62 |
Create Accounts
Firstly, we treat the house as an Asset. Since the house is being listed as an Asset, it needs to be given a unit. In this case, the unit quantity is only one, it's unlikely there will be multiple, and even if it's the nth house, we would want to record it in a separate Asset. That is to say, one house corresponds to one Asset, and this Asset has a special unit, its value can only possibly be 1.
2019-12-31 commodity HOUSE.ABC
name: "123 ABC Street, XYZ City, CA, 12345"
2019-12-31 open Assets:Property:US:CA:123ABC HOUSE.ABC
2019-12-31 open Liabilities:Bank:US:SomeBank:Mortgage:Loan USD
In the first line here, we defined a commodity unit representing the house. In the fourth line, we defined an Asset account, which holds the commodity unit previously defined as the house. In the fifth line, we defined an account for the lending bank. As it's a liability, it falls under the Liabilities category.
Purchase
With the accounts set up as above, the act of buying a house is equivalent to
borrowing money (debt) + spending money (down payment) = 1 house in asset
The most important reference when buying a property is likely the Buyer’s Settlement Statement, which clearly outlines the flow of money.
2020-01-01 * "Buying the house"
Assets:Property:US:CA:123ABC 1 HOUSE.ABC {1,000,000 USD}
Assets:Bank:US:SomeBankA -100,000 USD
Assets:Bank:US:SomeBankB -101,000 USD
Liabilities:Bank:US:SomeBank:Mortgage:Loan -800,000.00 USD
Expenses:Home:Insurance 1,000 USD
Expenses:Home:Mortgage:Loan:ClosingCost
Here, we're detailing the transaction of buying the house, where money flows out from some banks (used for down payment and other expenses), a loan is taken (adding to liabilities), and a house is gained (added to assets).
Pay back mortgages
Based on the above purchase record, we currently owe 800,000 USD. Due to the interest, and considering that all loans in the US are amortized equally in terms of principal and interest, the monthly payment includes a portion for interest and a portion for principal. In the early stages, the interest constitutes the majority.
To record the loan repayment, all you need to do is check your loan bank's statement. You just need to know how much of the principal you are repaying each month, and the rest is interest. The interest is counted as an Expense.
2020-02-01 * "Mortgage payment"
Assets:Bank:US:SomeBank:Saving:Joint -3,372.83 USD
Liabilities:Bank:US:SomeBank:Mortgage:Loan 1,376.26 USD
Expenses:Home:Mortgage:Loan:Interest
This entry details the monthly mortgage payment which is subtracted from your joint savings account. The repayment of principal reduces the liability, while the interest part is treated as an expense.
Appreciation
If you want to record the appreciation of the property, some people create a separate account[, only recording the appreciation of the current property. Considering that the value of the house may increase or decrease, this appreciation may be negative. The advantage of this is that in the summary of your total assets, these two accounts will be included, one for the value of the house at the time of the transaction, and the other for the current appreciation of the house, thus reflecting the real-time price of the house.
I did not adopt this method, mainly for the following reasons:
- The current value of the house can only be an estimate, for reference only, without practical value. Usually, I can only get the evaluation of the property on websites like Redfin or Zillow, and I personally don't think it has high reference value. I also did not consider incorporating these appreciations into total assets in real time.
- Personally, I think before the mortgage is paid off, if the cash flow of the house is negative, to some extent, the property is still a liability. Therefore, incorporating it into assets prematurely will give you an illusion of enriched assets and appreciation, and I personally want to avoid this illusion.
The method I use to record property appreciation, which will also be discussed later on how to model RSUs. This method is to use a virtual currency unit. Assuming your base currency is USD, we can use USD.UNVEST (it seems that there is no need to create a new Commodity for this) to indicate that this asset is calculated in a special currency. The growth or reduction of this asset will not be recorded in USD. This way, I can achieve my original goal, that is, to record the appreciation of the house, and this appreciation will not be included in the final balance sheet (Balance Sheet).
2020-01-01 price HOUSE.ABC 1,000,000 USD
2025-01-01 price HOUSE.ABC 1,400,000 USD.UNVEST
You only need to price your property to USD.UNVEST regularly.
So, on Fava's Commodity page, you can track the trend of the reference price of the house. But on the Balance Sheet page, the price of the house is still the price of the house at the time of the transaction. That is to say, your total assets are still your down payment money at that time, plus the principal you keep paying off. The final change of this asset should only occur when you buy a house.
Sell
Because no property has been sold yet and the various miscellaneous fees in the middle are unclear, this is a hypothetical scenario.
Suppose, on January 1, 2025, the property has appreciated to $1,400,000, and some reference data are as follows:
| Item | Amount |
|---|---|
| Balance | 709,656.20 |
| Agent fee (6%) | 72,000 |
| Other Closing Fee | 10,000 |
Person A decides to sell the property, and the final selling price of the house is $1,300,000.
2025-01-01 * "Selling the house"
Assets:Property:US:CA:123ABC -1 HOUSE.ABC {1,300,000 USD}
Liabilities:Bank:US:SomeBank:Mortgage:Loan 709,656.20 USD
Expenses:Home:Agent:Fee 72,000 USD
Expenses:Home:ClosingCost 10,000 USD
Expenses:Home:Tax 90,000 USD
Assets:Bank:US:SomeBankA
Here it is assumed that 2 out of 5 years are self-occupied, so the appreciation of 500,000 does not need to be taxed. I randomly calculated a number here. In the end, the money that enters Person A's account is $418,343.8, of which 200,000 is the down payment at that time, and about 100,000 in interest has been paid. So, in the end, the book profit for Person A is around 100,000. It is worth noting that my calculation is not fair, after all, Person A has saved rent for these 5 years, and there may be other expenses on the house, such as maintenance, decoration, and so on.
To reflect this in the balance sheet, you can add this pricing.
2025-01-01 price HOUSE.ABC 1,300,000 USD



